Exploring the World of Kaspa: Features, Developments, and Future Horizons
![]() Sarah Rodriguez • 07 Dec 2023
Sarah Rodriguez • 07 Dec 2023

In the dynamic world of blockchain and cryptocurrencies, Kaspa stands out as a groundbreaking project, redefining the boundaries of blockchain technology. Merging the time-tested security of Proof-of-Work (PoW) mechanisms with unprecedented high block rates and minimal confirmation times, Kaspa represents a new frontier in decentralized network architecture. With its innovative approach and commitment to scalability, Kaspa is swiftly emerging as a potential game-changer in the realm of decentralized applications.
Kaspa (KAS) has experienced a remarkably positive trajectory over the past nine months, marking its presence as a robust and thriving entity in the cryptocurrency markets. But what exactly underpins this burgeoning blockchain network? At its core, Kaspa is built on a PoW consensus mechanism, augmented by a Block Directed Acyclic Graph (blockDAG) structure. This unique composition allows for multiple blocks to coexist in parallel, effectively addressing the high orphan rate issue commonly encountered in traditional blockchain systems. In essence, this structure ensures that when two blocks are mined simultaneously, both can be accepted and utilized by the network, a significant leap from the limitations of linear blockchain models.
Drawing inspiration from the visionary Satoshi Nakamoto, Kaspa aims to uphold the foundational principles of the Bitcoin (BTC) consensus. This includes maintaining a proof-of-work mining system, implementing a deflationary monetary policy, and ensuring decentralized governance. By staying true to these core elements while innovating in key areas, Kaspa is poised to honor the legacy of Bitcoin while carving out its own distinct path in the cryptocurrency landscape.
What is Kaspa
Kaspa, initially developed by DAGLabs with support from PolyChain, has evolved into a community-driven project with no central governance. Founded by Yonatan Sompolinsky, a notable figure in blockchain research and a Postdoctoral Computer Scientist at Harvard University, Kaspa stands out for its innovative approach to blockchain technology.
The development team, a blend of academic and technical experts, drives Kaspa's progress.
Kaspa is recognized as the fastest and most scalable transaction layer built on a proof-of-work engine, distinguished by its blockDAG structure. This allows for immediate inclusion of transactions in the ledger and is based on the scalable GhostDAG/PHANTOM protocol, a generalization of Bitcoin's Nakamoto Consensus.
Faithful to Bitcoin’s principles, Kaspa incorporates proof-of-work mining, a UTXO-formed isolated state, deflationary monetary policy, and decentralized governance. The mainnet currently operates at one block per second, with plans to substantially increase this rate post-Rust language rewrite, opening doors for smart contracts and DeFi applications.
Main Features of Kaspa
 image source: https://kaspa.org/
image source: https://kaspa.org/
High Transaction Speed
One of the critical challenges in the widespread adoption of popular cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum has been their limited transaction speed. This slow pace, inherent in the design of linear blockchains, has been a significant roadblock to their use in everyday transactions. The linear structure of these blockchains simply cannot process transactions quickly enough to meet the demands of high-frequency, real-world usage.
Kaspa addresses this bottleneck with its innovative "blockDAG" approach. This method, distinct from the traditional linear blockchain model, allows for the creation of multiple blocks every second. The result is a significant acceleration in the transaction process, enabling entries into the network to be ready for confirmation almost instantaneously. We will dive deeper into the blockDAG technology and its implications in the next part below.
As a result, Kaspa emerges as a game-changer in the cryptocurrency world, offering the high transaction speed necessary for mass adoption and practical, everyday use. Its ability to process transactions at such a rapid rate marks a departure from the limitations of conventional blockchain designs, paving the way for a more efficient and scalable digital currency system.
BlockDAG: Revolutionizing Blockchain Technology
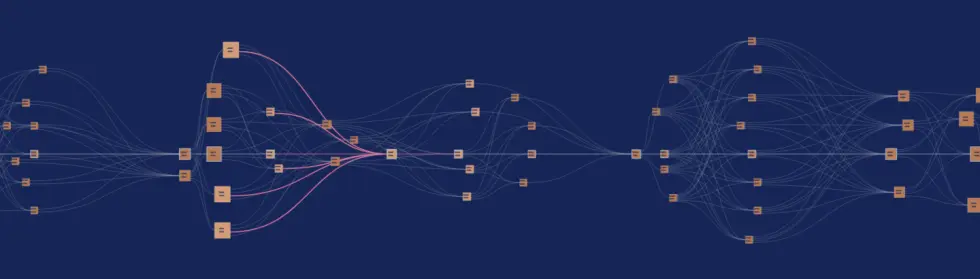 image source: https://kaspa.org/features/
image source: https://kaspa.org/features/
The concept of a Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) is fundamental to understanding the innovative leap Kaspa has taken with its BlockDAG technology. At its core, a DAG is a mathematical model characterized by vertices and edges, forming a directional graph that doesn't loop back onto itself. In the realm of distributed ledgers, a BlockDAG applies this concept to blockchain architecture: its vertices represent individual blocks, while edges denote references from blocks to their predecessors.
BlockDAG technology is designed to address the inherent limitations of linear blockchains and the traditional Nakamoto consensus. These limitations include scalability issues, the problem of selfish mining, and the creation of orphan blocks. In a stark departure from the linear model of traditional blockchains, where blocks reference only the single predecessor at the tip of the longest chain, BlockDAGs can reference multiple predecessors. This means that blocks in a BlockDAG reference all the tips of the graph, not just the longest chain's tip. This inclusive approach allows BlockDAGs to incorporate blocks from different branches, eliminating the concept of wasted or orphaned blocks.
The result is a more efficient and inclusive ledger system. In the BlockDAG model, no blocks are discarded; every block is published to the ledger, ensuring that no mining power goes to waste. This structure allows for more frequent block generation, which in turn facilitates a higher volume of transactions and leads to near-instantaneous confirmations.
But how does Kaspa achieve this remarkable efficiency? The key lies in its deviation from the longest chain consensus method and the adoption of the GhostDAG (Phantom 2.0) consensus mechanism. This novel approach allows for a more holistic and information-rich block mining process. By mining a block and sharing all known block tips, miners maximize the information relayed across the network, adhering to the principle of maximal revelation.
BlockDAGs represent a significant advancement over both singular and parallel blockchain models. Their ability to convey maximum information and utilize every mined block gives them a distinct edge in efficiency and scalability, making them a superior choice for modern blockchain applications.
Scalability: Kaspa's Solution to High-Volume Transactions
Scalability is a pivotal aspect of any blockchain network, particularly when considering its capacity to handle a vast number of transactions and users simultaneously. The ability to maintain fast block ledger speeds and instant confirmations, regardless of the user volume, is a critical factor in determining a blockchain's effectiveness and reliability. This challenge is especially pertinent in scenarios involving thousands, hundreds of thousands, or even millions to billions of users transacting at the same time. Most traditional blockchain networks struggle with these conditions, often becoming clogged and less efficient under high transaction loads.
Kaspa, with its innovative blockDAG design, presents a formidable solution to these scalability challenges. The blockDAG framework enables Kaspa to handle large volumes of transactions within very short periods. This is achieved through the simultaneous creation of multiple blocks at an astonishing average rate of one block every second. Such a high block generation rate is unprecedented, especially in a purely decentralized proof-of-work network.
This ability to rapidly process a large number of transactions within brief durations is a unique attribute of Kaspa, distinguishing it from other blockchain systems. Its design not only ensures efficiency and speed but also maintains the integrity and decentralized nature of the network. By effectively addressing the scalability issues inherent in most blockchains, Kaspa stands as a groundbreaking model for high-volume, decentralized transaction processing.
Efficient Proof-of-Work: Kaspa's Eco-Friendly Approach
In the realm of blockchain technology, the proof-of-work (PoW) mechanism is often scrutinized for its environmental impact. Kaspa, however, stands out as a “pure" PoW and decentralized digital asset that doesn't compromise on either efficiency or decentralization. In an era where many projects are leaning away from decentralization for scalability and speed, Kaspa has innovatively addressed these challenges within a truly decentralized framework.
Decentralization lies at the heart of cryptocurrencies, ensuring freedom from manipulation by central entities and large stakeholders. To preserve this core principle while mitigating the environmental concerns associated with mining, Kaspa has adopted kHeavyHash. This algorithm is a highly efficient 'core heavy' algorithm, notable for its exceptional hashing power per watt, a stark contrast to most PoW algorithms like ETHash, SHA-256, and KawPow. kHeavyHash's efficiency is a step forward in eco-friendly blockchain technology and is also compatible with future optical mining systems, which could further reduce energy consumption.
Furthermore, Kaspa’s BlockDAG architecture plays a crucial role in its energy-efficient design. Unlike linear blockchains like Bitcoin, which regularly encounter and discard duplicate blocks, thus wasting significant computational power, Kaspa’s BlockDAG ensures that every block and chain contributes to network security. No blocks are discarded in Kaspa's system, meaning that every bit of computational effort is utilized, enhancing both the efficiency and ecological footprint of the network.
Kaspa's choice of kHeavyHash, combined with its BlockDAG structure, underscores its commitment to maintaining a decentralized, secure, and environmentally considerate blockchain network. It represents a harmonious balance between the foundational principles of cryptocurrency and the pressing need for sustainability in the digital age.
Security in Kaspa: Strengthened by kHeavyHash
Kaspa prioritizes security by aligning with Bitcoin's proven methodologies, but with a significant enhancement in its proof-of-work (PoW) encryption: the adoption of kHeavyHash. This modified version of the SHA-256 algorithm, fortified with an additional weighting function, inherits the robust security properties of SHA-256, ensuring Kaspa's network remains highly secure.
The integration of kHeavyHash into Kaspa’s BlockDAG structure is central to its security strategy. This approach engages a network of decentralized miners who validate and sign transactions, similar to Bitcoin’s model. The decentralized nature of Kaspa ensures that anyone can participate in and help secure the network, reinforcing its security through collective effort and transparency.
Kaspa's commitment to security is reflected in its choice of kHeavyHash and its decentralized, permissionless infrastructure, making it a resilient and secure blockchain platform for digital transactions.
Technologies Behind Kaspa Currency
Embracing the Nakamoto Consensus
Kaspa aligns itself with the Nakamoto Consensus, the original consensus engine named after Bitcoin's creator, Satoshi Nakamoto. This pioneering consensus model, based on a proof-of-work (PoW) mechanism, has been securing the Bitcoin network and other well-known PoW cryptocurrencies like Litecoin, Bitcoin Cash, and ZCash.
The strength of the Nakamoto consensus lies in its proven security properties. These properties are not only mathematically sound but have also been practically validated over 14 years of Bitcoin's operation, without any major incidents. The security premise is simple yet effective: to exploit the blockchain, an actor would need to control over 50% of the network's hashrate, a task that becomes increasingly infeasible as the network grows. This inherent security is a key reason for the continued high trust in Bitcoin and its adoption by mainstream institutions as both a store of value and a payment system.
In contrast to the Nakamoto consensus, many newer blockchain models have adopted proof-of-stake (PoS) consensus mechanisms, prioritizing scalability and speed, often at the expense of decentralization. Kaspa, however, upholds the Nakamoto consensus for its robust security framework and commitment to decentralization, ensuring it stays true to the foundational principles that underpin the trust and efficacy of blockchain technology.
GhostDAG: Enhancing Consensus in Kaspa
The Evolution from PHANTOM to GhostDAG
GhostDAG stands as a pivotal consensus mechanism within Kaspa, evolving from and improving upon the PHANTOM consensus. While PHANTOM is based on solving an NP-hard problem and is not practical on its own, GhostDAG utilizes the underlying intuition of PHANTOM to create a more efficient, implementable algorithm.
Security and Order of Transactions
A key aspect of GhostDAG's security is the formal proof that its block ordering becomes exponentially difficult to reverse over time. This security feature is crucial, especially considering the high block creation rate relative to network propagation delays. The core principle here is that as long as the majority of computational power is in the hands of honest nodes, the probability of changing the order of transactions (tx1, tx2) embedded in the blockDAG diminishes exponentially with time.
The k-Cluster and Greedy Algorithm Approach
GhostDAG diverges from PHANTOM in how it selects a k-cluster, leading to the categorization of blocks as Blues (within the selected cluster) and Reds (outside the cluster). Instead of seeking the largest k-cluster, GhostDAG employs a greedy algorithm. This algorithm constructs the Blue set of the DAG by initially inheriting the Blue set from the best tip (Bmax - the tip with the largest Blue set in its past). It then adds blocks outside Bmax’s past, maintaining the k-cluster property.
Chain Induction and Final Order
This greedy inheritance rule used by GhostDAG induces a chain. The last block in this chain is Bmax, followed by the selected tip of the DAG past Bmax, and so on, down to the genesis. This chain is denoted as Chn(G). The final ordering of blocks in GhostDAG mirrors the coloring procedure: it inherits the order of Bmax on blocks in its past, adds Bmax to the order, and then incorporates blocks outside past Bmax in a topological manner. This approach ensures that the order over blocks becomes robust and reliable as the coloring procedure progresses.
Pruning: Streamlining Kaspa's BlockDAG
The Need for Pruning in Kaspa
In Kaspa, pruning is an essential technique utilized to manage the size of the blockDAG efficiently. Given the high block creation rate in Kaspa's network, the blockDAG could potentially grow to unwieldy sizes. Pruning helps to alleviate this issue by reducing the volume of blockDAG data that nodes need to store. This is particularly important in Kaspa, where the blockDAG, due to its structure and frequency of block generation, could otherwise demand substantial storage capacity.
How Pruning Works in Kaspa
Thanks to the pruning mechanism, Kaspa nodes are required to store only about three days' worth of historical data. This significantly reduces the storage demands on individual nodes, facilitating the creation and maintenance of numerous nodes within the network without imposing large storage requirements.
Unique Approach to Pruning
The pruning mechanism in Kaspa is specifically tailored to its unique blockDAG and GhostDAG consensus architecture. The design of Kaspa's pruning algorithm focuses on resistance to attacks, particularly from actors controlling a significant but minority portion of the network's hash rate (up to 49%). The approach integrates concepts of finality and invalidation rules:
Finality: This involves setting a fixed depth beyond which reorganizations (reorgs) of the blockDAG are not allowed. While non-finalized blocks may not be pruned, finalized blocks also might need to be retained if their data are necessary for computing the UTXO set of incoming blocks.
Invalidation Rules: Kaspa employs three key invalidation rules:
- If a block is invalid, then any block pointing to it is also considered invalid. Blocks deemed invalid are discarded.
- A block is deemed invalid if it contains another block in its past that is also in its anticone and lacks a 'kosherizing' block.
- The 'Bounded Merge' rule limits the size of merged sets of blocks. It restricts the set of blocks in a block's past that are neither its selected parent nor in its selected parent's past, using a fixed parameter, L.
These rules and mechanisms ensure the pruning process in Kaspa is efficient and secure, maintaining the integrity of the network while optimizing its scalability and performance.
Current Development and Latest Updates in Kaspa
Completed Stage:
Dag Knight Consensus Research Publication
Kaspa has completed a research paper on a revolutionary new consensus mechanism, potentially set to be integrated into the network. This mechanism, known as DagKnight consensus, is an evolution of the existing GHOSTDAG protocol and promises to significantly enhance transaction speed and confirmation times. This research is a crucial step in Kaspa's ongoing development.
Development Stage:
DAGKNIGHT: A New Consensus Protocol
DAGKNIGHT (DK) is a cutting-edge consensus protocol developed under this KIP (Kaspa Improvement Proposal). It's designed for enhanced responsiveness and boasts a 50% Byzantine tolerance, making it faster and more secure than the current GHOSTDAG (GD) protocol. Unlike GD, DK doesn’t rely on a hardcoded parameter k, allowing it to adapt dynamically to the actual network conditions. This flexibility will enable clients and wallets to tailor their transaction confirmation policies more effectively, akin to the variable confirmation requirements seen in Bitcoin.
2023 White Paper
While Kaspa's technology has been the subject of numerous research papers, an official white paper is scheduled for release in 2023. This comprehensive document will consolidate Kaspa’s past research and current objectives into an accessible and detailed guide, aimed at educating newcomers and onboarding developers to the Kaspa ecosystem.
Archival Node Improvements
Kaspa is working on significant enhancements to its archival nodes. The current absence of P2P communication in these nodes limits the exchange of normally pruned data. The upcoming improvements will enable a more extensive block explorer capability, allowing users to access transaction history beyond the standard three-day limit imposed by Kaspa’s pruning mechanism. This advancement will facilitate access to more extensive historical data, significantly improving the network's utility and research potential.
Testing Stage:
KASPA Rust Language Coding
Kaspa is currently undergoing a significant transition, with its programming language being shifted from GoLang to Rust. This critical development, spearheaded by developer Michael Sutton, is set to substantially enhance Kaspa's performance and speed. The transition to Rust is anticipated to enable groundbreaking transaction rates and blocks per second, with conservative estimates pointing towards achieving around 10 blocks per second (bps). This rewrite is not just a technical upgrade; it lays the groundwork for Kaspa's ambitious future goal of reaching 100 bps.
Rust, known for its high-performance capabilities, allows for the implementation of sophisticated and hardware-optimized features, such as parallelism. This means different blocks can be processed simultaneously across multiple CPU threads, a stark contrast to the current GoLang model, likened to modeling clay for its role in shaping and proving concepts. The shift to Rust is akin to moving from modeling clay to artisan-grade ceramics, offering refined, durable, and efficient performance.
Integration of Kaspa on Ledger
Following a successful 24-hour fundraising blitz, development efforts are now underway to integrate Kaspa with Ledger, a leading hardware wallet platform. This integration aims to provide a quick, secure, and user-friendly method for sending and receiving $KAS. The move to enable $KAS holdings on Ledger is a strategic step towards achieving Kaspa's goal of creating a widely accepted and secure currency. It underscores Kaspa's commitment to providing safe and convenient transaction methods for its users, further solidifying its position as a reliable digital currency.
Plans Stage:
Smart Contracts Implementation
As Kaspa strives to solidify its position as the fastest, most scalable, and secure Layer 1 (L1) Proof-of-Work (PoW) cryptocurrency, the team acknowledges that while significant milestones have been achieved, there remains room for fine-tuning to attain peak performance. However, Kaspa's vision extends far beyond mere performance metrics. The ultimate aim is to establish Kaspa as the premier L1 platform for implementing smart contracts, decentralized finance (DeFi), and Layer 2 applications.
This ambition is not just about technological advancement but also about fostering a vibrant ecosystem. Kaspa envisions a future where a robust ecosystem, built on its efficient and secure platform, thrives and evolves. This ecosystem is expected to be as strong and dynamic as the foundation laid by Kaspa's technology and the dedicated community that has been instrumental in its development.
For the latest news and more information on Kaspa's exploration of smart contracts, visit Kaspa's official website.
News: Kaspa's Expanding Reach
Recent Listings and Enhanced Exchange Options
Exchangio Crypto Exchange Service
Kaspa has recently been listed on Exchangio, a significant milestone for the cryptocurrency. Users can now exchange Kaspa with over 700 other assets on the Exchangio platform. These exchanges are designed to be fast and user-friendly, requiring no registration, thus offering a seamless trading experience. For those interested in trading Bitcoin for Kaspa, the process has been made simple and efficient. You can swap BTC to KAS directly on Exchangio, ensuring quick and hassle-free transactions.
AltCoinTrader
Kaspa's reach continues to grow with its addition to AltCoinTrader, another popular cryptocurrency trading platform. This listing further enhances Kaspa's visibility in the crypto market and provides users with additional avenues to access and trade Kaspa.
Bitrue
Kaspa is also now available on Bitrue, expanding its availability to a wider audience and offering more opportunities for trading and investment. This listing is part of Kaspa's ongoing effort to increase its presence and accessibility in the global cryptocurrency market.
Conclusion: Kaspa's Path Forward
As we reflect on the journey of Kaspa, it's clear that this innovative blockchain project has made significant strides in redefining the capabilities of decentralized digital currencies. From its high transaction speeds and scalable BlockDAG architecture to the efficient and secure proof-of-work mechanism with kHeavyHash, Kaspa has consistently pushed the boundaries of what's possible in blockchain technology.
The development of the DAGKNIGHT consensus protocol and the ongoing transition to Rust programming highlight Kaspa's commitment to continuous improvement and technological advancement. The anticipated release of the 2023 white paper and the enhancements to archival nodes promise to provide deeper insights into Kaspa’s technology and expand its functionality.
Kaspa’s recent listings on prominent crypto exchanges like Exchangio, AltCoinTrader, and Bitrue mark a significant milestone in its growth, enhancing its visibility and accessibility to a broader audience. These developments not only increase Kaspa's presence in the cryptocurrency market but also offer users more opportunities for engagement and investment.
Looking ahead, Kaspa's plans to implement smart contracts and develop a robust ecosystem for DeFi and Layer 2 applications set an ambitious course for the future. The vision of creating a strong, versatile platform on the solid foundation laid by its technology and community holds great promise.
Disclaimer:
The information contained in this article is provided for educational and informational purposes only. It is not intended to be investment or financial advice, and should not be taken as such. Cryptocurrency is a highly speculative and volatile market, and any investment made in it carries a significant risk. Before making any investment decisions, it is recommended that you seek the advice of a qualified financial professional to understand the potential risks and rewards associated with investing in cryptocurrencies.
