What is a Bitcoin fork?
![]() Sarah Rodriguez • 15 Dec 2023
Sarah Rodriguez • 15 Dec 2023

Ah, Bitcoin forks, the apples of the cryptocurrency tree. They're like those distant relatives who decided to go their way and start a slightly different family. Fascinating. In this blog, we'll take a joyride down the twisted roads of Bitcoin Fork, exploring the evolution of Bitcoin's offspring.
But first, let's clear the air. What is a Bitcoin fork? Hold tight, folks, because we'll unravel some captivating tales of cryptocurrencies. From the birth of Bitcoin Cash to the controversial Bitcoin SV shenanigans and everything in between, this blog will guide you through the intricate maze of Bitcoin offspring.
What is a Fork in Cryptocurrency?
Ah, the wonderful world of forks! No, we’re not talking about the utensils you use to eat pasta, although that would make for a rather interesting blog. In the realm of the cryptocurrency universe, a fork refers to a splitting of the blockchain. Confused? No worries, we’ll break it down for you.
Importance of Understanding Bitcoin Forks
Understanding bitcoin forks is crucial in cryptocurrency because it helps investors avoid potential losses. It can affect the value of both the existing cryptocurrency and the new one created. As a result, it is essential to have a basic understanding of forks and how they work.
Why Do We Need Bitcoin Forks?
Common reasons include:
- Growing blockchain pains. When a cryptocurrency's blockchain expands, it offers a quick fix by creating a faster network, counting transactions like when users (href="https://exchang.io/exchange-pairs/btc-to-usdt")exchange BTC to USDTfrom the fork's inception.
- Network upgrades. Developers can tweak block sizes and hashing algorithms to boost blockchain speed and security.
- Crypto clashes. Disagreements in the community can spark Bitcoin forks as factions debate how the blockchain should operate.
Bitcoin Fork History: The Birth of a New Bitcoin
Bitcoin, the pioneer of cryptocurrencies, has seen significant transformations throughout its history. Each fork represents a pivotal moment, giving birth to a new version of Bitcoin and shaping its evolution. Let's delve into the intriguing chronicle of Bitcoin forks, where innovation meets the consensus challenge.
Genesis of Forks
Forking in the Bitcoin ecosystem arises from the need for upgrades, optimizations, and addressing divergent viewpoints within the community. A fork is essentially a split in the blockchain, creating a distinct and independent cryptocurrency.
Bitcoin XT: A Trailblazer in 2014
One of the early forks that left its mark on Bitcoin's trajectory is Bitcoin XT, initiated by Mike Hearn in 2014. Unlike other forks, which primarily focused on block size adjustments, Bitcoin XT introduced protocol optimizations unrelated to block sizes, showcasing the diverse avenues for innovation within the blockchain.
BIP 101 and the Quest for Scalability
In 2015, Gavin Andresen proposed BIP(Bitcoin Improvement Proposal) 101, a bold move to address Bitcoin's scaling issues amid rising transaction volumes. BIP 101 aimed for a substantial block size increase from 1 to 8 MB, with a roadmap envisioning a gradual rise to 24 transactions per second. Despite the optimism, this proposal faced the challenge of garnering 75% network support, a hurdle it needed help to overcome. The community opted for an alternative 2 MB increase inspired by Bitcoin Classic, marking a turning point in Bitcoin's scalability journey.
The Evolution Continues
These forks illustrate the dynamic nature of Bitcoin's development, where ideas clash, consensus is tested, and the blockchain adapts. As the cryptocurrency landscape continues to evolve, the chronicle of Bitcoin forks becomes a captivating narrative of innovation, challenges, and the relentless pursuit of improvement.
Types of Bitcoin Forks
The world's most popular cryptocurrency has a complex ecosystem that evolves with time. One way that Bitcoin evolves is through a process called "forking." During a fork, the existing blockchain splits into two separate chains, each following its own rules. These occur because of ideological differences within the Bitcoin community, enabling new features and upgrades to the network.
There are two types of forks: Hard and Soft.
Hard Forks: Definition and Explanation
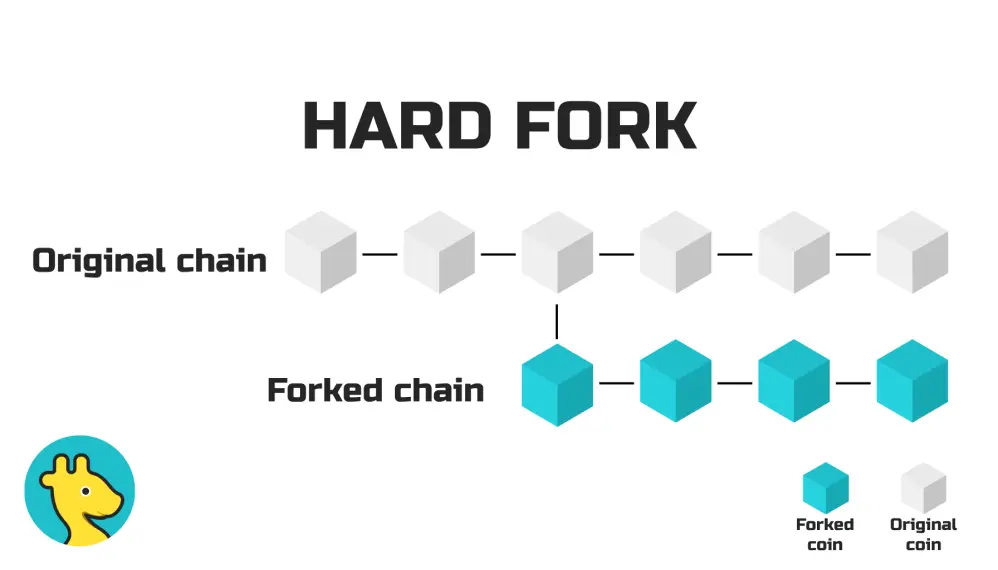
Hard forks are significant changes to the Bitcoin protocol. These changes change the rules of the network such that the existing blockchain is no longer compatible with the latest version. When this happens, the blockchain is divided into two branches, each with its own rules. Hard forks can result from changes in the consensus rules or a decision to branch off the existing blockchain.
Soft Forks: Definition and Explanation
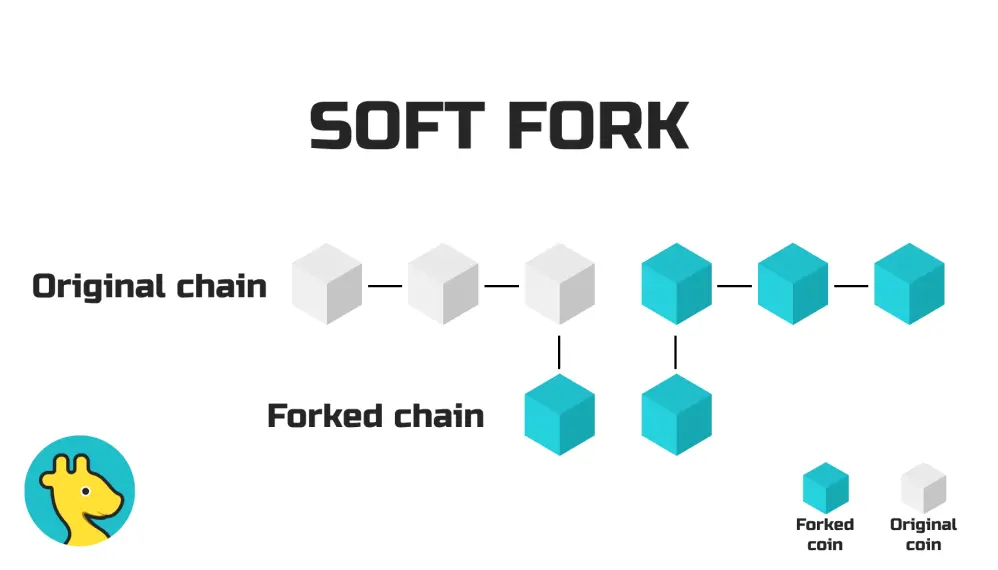
On the other hand, soft are minor changes to the Bitcoin protocol. The changes made in a soft fork do not make the existing blockchain incompatible with the new version. Instead, they are backward compatible, meaning that they work with both the old version of the blockchain and the new one.
What are the Differences Between a Hard and a Soft Fork
Blockchain updates or protocol changes come in two primary forms: hard and soft forks. A hard fork involves the creation of an entirely new chain, while a soft fork is an optional update that maintains backward compatibility with the existing chain.
The critical factor behind a hard fork is the absence of backward compatibility. When miners on the new update generate blocks, those on the old chain will not accept these blocks, resulting in the emergence of a new independent chain. Hard forks typically entail protocol changes or modifications to rules. On the other hand, soft, exemplified by optimizations like Segregated Witness (SegWit), does not give rise to a new chain and is more focused on enhancing efficiency while remaining backward compatible with the existing network.
It's important to note that while hard creates a clear split, soft offers a more flexible approach, allowing participants to choose whether or not to adopt the update. This distinction emphasizes the dynamic nature of blockchain development, where protocol changes can range from fundamental alterations to more incremental optimizations.
Bitcoin Main Forks
Bitcoin Cash

In the summer of 2017, Bitcoin underwent a significant fork, resulting in the birth of Bitcoin Cash. The main reason for this fork was the ongoing debate about the block size limit of Bitcoin. Some developers argued that the small block size of Bitcoin was restricting the number of transactions that could be processed at any given time, leading to delays and high transaction fees when users try to exchange BTC.
As a solution, Bitcoin Cash was created, with a block size limit of 8 MB compared to the 1 MB limit of Bitcoin. This allowed for faster transaction processing times and lower fees, making it a more attractive option for users.
The impact of Bitcoin Cash on the crypto industry was significant, as it quickly became one of the top cryptocurrencies by market capitalization. Its success sparked a debate within the crypto community about the importance of block size limits and how they affect the overall scalability of Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies.
Bitcoin Gold

Bitcoin Gold emerged in 2017 as a response to Bitcoin's increasing mining difficulty and centralization of mining power in China. The goal of Bitcoin Gold was to become a more decentralized version of Bitcoin that would be more accessible to individual miners using their home computers.
One key difference between Bitcoin and Bitcoin Gold is the mining algorithm used. Bitcoin uses the SHA-256 algorithm, while Bitcoin Gold uses Equihash. This change allows more miners to participate in the network, as specialized mining hardware is not required.
The impact of Bitcoin Gold on the crypto industry has been mixed. Some argue that it has contributed to further fragmentation of the Bitcoin network, while others see it as a necessary step towards a more decentralized future. Despite this, Bitcoin Gold has a dedicated following and has maintained a spot in the top 100 cryptocurrencies by market cap.
Bitcoin Diamond
Bitcoin Diamond is a cryptocurrency that was created in 2017 as a hard fork of the Bitcoin blockchain. It aims to address issues such as slow transaction speeds and high fees associated with Bitcoin.
Bitcoin Diamond uses a larger block size than Bitcoin, which allows for faster and cheaper transactions. It also incorporates advanced security measures, such as encryption and decentralization, to protect users' funds.
One of the key features of Bitcoin Diamond is its compatibility with existing Bitcoin wallets, making it easy for users to adopt the new currency. Additionally, it has a total supply of 210 million tokens, which provides more excellent stability than Bitcoin's limited supply of 21 million.
Bitcoin Classic
Bitcoin Classic was a fork of the Bitcoin blockchain that happened in February 2016. Its main objective was to increase Bitcoin's transaction processing capacity by increasing the block size limit. Bitcoin Classic started with a block size limit of 2 MB, which was later expanded to 8 MB. It received much support from the Bitcoin community, significantly increasing its market value.
However, despite its popularity, Bitcoin Classic was discontinued in November 2017 due to a lack of further development and support. Despite its discontinuation, Bitcoin Classic played a significant role in shaping the future of Bitcoin by initiating the debate on scalability and bringing into the limelight the importance of finding a long-term solution to the issue.
Final Thoughts
In brief, This, resembling a family drama in the crypto tree, has shaped its evolution. From early optimizations to scalability proposals, each fork marks a unique chapter. Understanding their impact is crucial in addressing blockchain growth, upgrades, and community clashes. Hard creates new chains, while soft maintains compatibility, showcasing the dynamic nature of blockchain development. Examples like Bitcoin Cash, Bitcoin Gold, and others illustrate industry responses, sparking debates and shaping Bitcoin's future.
FAQ
What is a Bitcoin fork?
A blockchain split creates a new, independent cryptocurrency, often due to upgrades, optimizations, or community disagreements.
What are the types of Bitcoin forks?
Two main types - hard create new chains with rule changes, while soft are backward-compatible updates maintaining harmony with the existing chain.
Are Bitcoin forks still happening?
Yes, the story of Bitcoin forks continues as the dynamic nature of blockchain development shapes the trajectory of Bitcoin with new challenges, innovations, and improvements.
Disclaimer:
The information contained in this article is provided for educational and informational purposes only. It is not intended to be investment or financial advice, and should not be taken as such. Cryptocurrency is a highly speculative and volatile market, and any investment made in it carries a significant risk. Before making any investment decisions, it is recommended that you seek the advice of a qualified financial professional to understand the potential risks and rewards associated with investing in cryptocurrencies.
